This page contains information on the various ways you can deploy the Translator.
You can deploy the Translator in several ways:
- Deploying a single instance of the Translator on a single server (or virtual server) may be acceptable for very simple applications that do not require high performance or failover support.
- Deploying multiple instances of the Translator on a single server (or virtual server) provides some failover support and is required for high performance applications. (If one Translator instance fails, then another Translator instance can continue the user session.) Increasing the number of Translator instances on a server is referred to as vertical scaling.
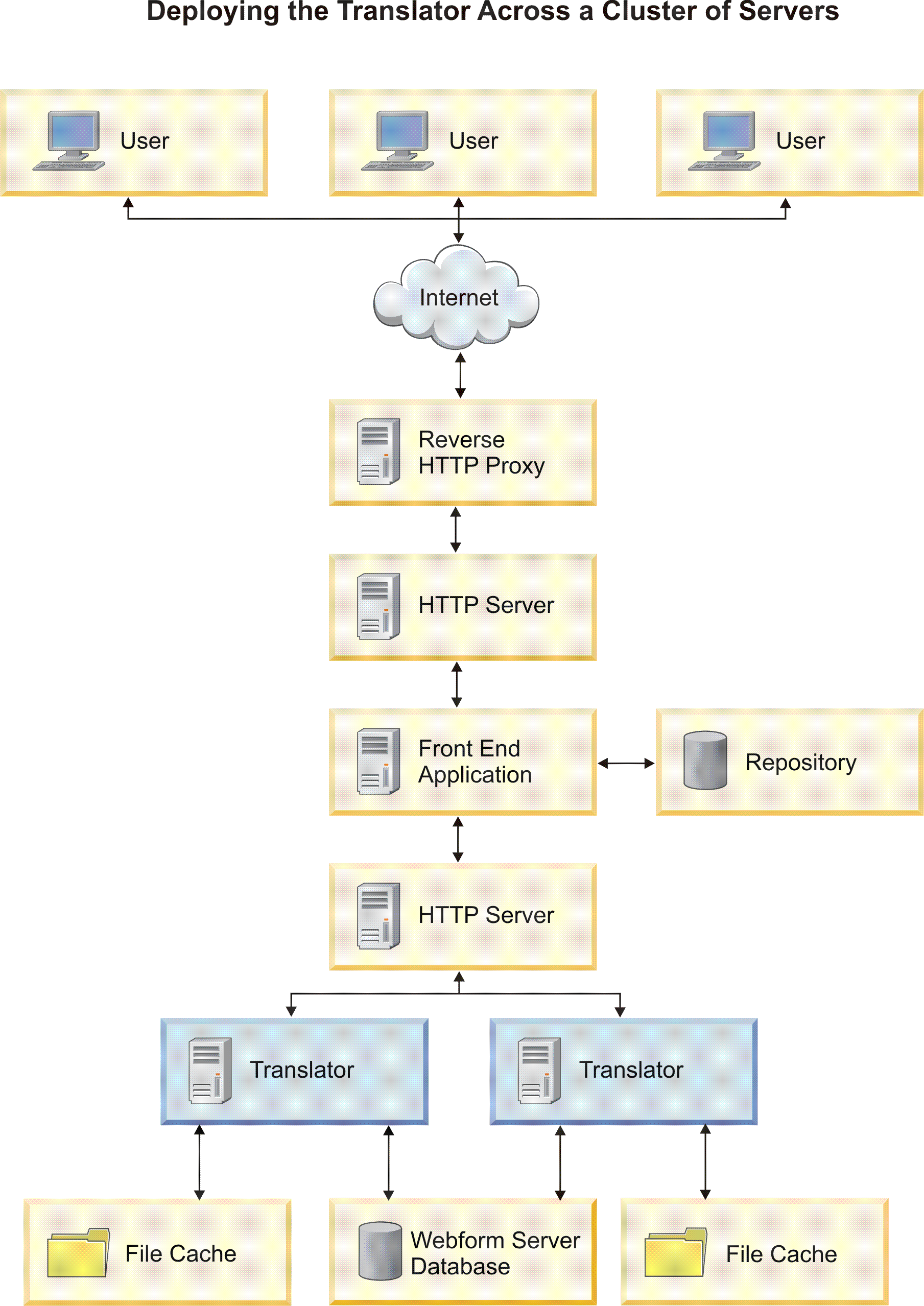
- Deploying multiple instances of the Translator across a cluster of servers (or virtual servers) provides increased failover support and may be required for some high performance applications. (If one Translator server fails, a Translator instance on another server can continue the user session.) Increasing the number of servers hosting Translator instances is referred to as horizontal scaling. If you deploy the Translator in this manner, you must provide load balancing between the servers (for example, using IBM® HTTP Server). You must also configure each instance of WebSphere® Application Server for clustering.
Use the following steps to help you setup, test and tune your Translator configuration:
- For your initial setup, start with one virtual server hosting
one instance of the Translator.
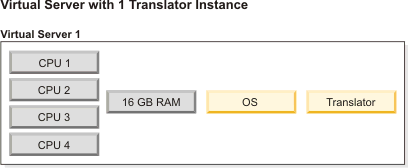
- After initial testing, adjust the Translator server configuration by increasing the number of Translator instances on the virtual server until the CPU or memory becomes 100% utilized.Note: Make sure each Translator instance has no less than 4 GB of physical memory available. For example, if your virtual server has 16 GB of memory, you can increase the number of Translator instances to a maximum of 4.
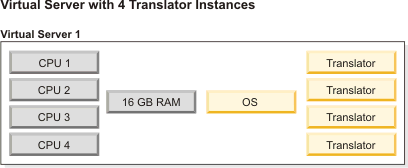
In general, the virtual server will become memory-bound (the memory is the bottleneck) for larger forms or CPU-bound (the CPU is the bottleneck) for smaller forms.
Occasionally, the virtual server will become I/O bound, especially when configured to provide better failover support, which requires frequent reading from and writing to the File Cache.
- Next, re-partition the server into a greater number of virtual
servers. For example, if your server has four CPUs, your inital configuration
would be 1 virtual server (with 4 CPUs) and your next configuration
would be 2 virtual servers (with 2 CPUs each). Note: High performance Webform Server applications require at least 2 CPUs per virtual server hosting Translator instances.
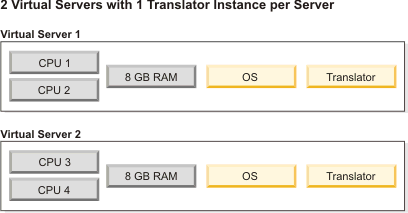
- Experiment with different combinations of virtual servers and
Translator instances until resources are fully utilized. Note: Your Webform Server application will become more complex as you increase the number of virtual servers and Translator instances. Keep in mind the management of your overall system.
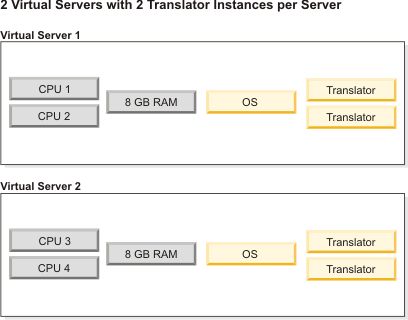
- If your Webform Server application
consists of several forms of various sizes, consider hosting smaller
forms on a dedicated virtual server and larger forms on a dedicated
virtual server. Performance is highly dependent upon form size and
design, so this will allow you tune each virtual server in different
ways. For example, each virtual server could have a different number
of Translator instances.
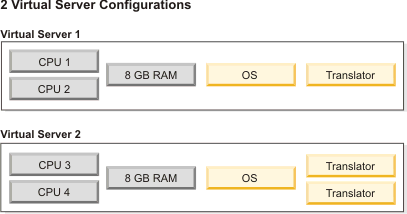
- If testing and tuning does not result in acceptable performance,
adjust your configuration as follows:
- If virtual servers are memory-bound, increase the amount of memory for the virtual server by adding physical memory to the server. Continue increasing the amount of physical memory until memory utilization falls just less than 100 percent.
- If virtual servers are CPU-bound, add more CPUs to the server or deploy an additional server for hosting Translator instances.